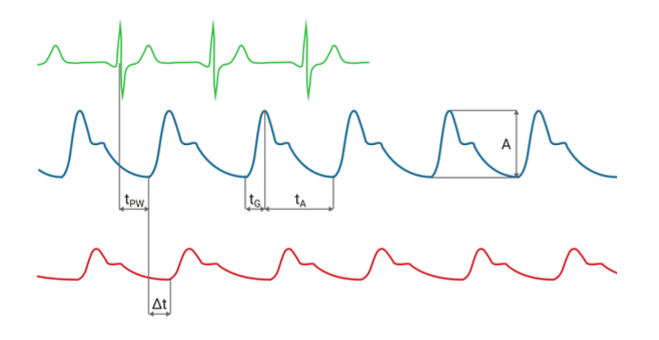
Pulse Wave Parameters
Additional key parameters and indicators can be derived from recorded pulse waves and ECG tracks:

- Amplitude A: The height from the beginning of the steepest rise to the highest point of the pulse curve is the amplitude.
- Oscillometric Index: The oscillometric index marks the pressure stage where the highest amplitude was measured and is comparable to the mean arterial pressure.
- Rise Time tG: The rise time marks the time interval of the steepest rise to the highest point of the pulse curve. Sometimes also referred to as “Peak Time” or “Time-To-Peak”.
- Fall Time tA: The fall time marks the time from the highest point of the pulse curve to the beginning of the next pulse curve.
- Rise to Fall: The quotient, stated in percentage, of rise time and fall time.
- Time Shift ∆t: The time shift, measured between the start point of both pulse curves, shows thepropagation time difference between the left and the right extremity.
- Pulse Transit/Propagation Time (PTT) tPW: The pulse propagation time is the time between the R-wave and the beginning of the pulse wave.
- Pulse Wave Velocity (PWV): The pulse wave velocity can be calculated using the propagation time and the measured distance. It is usually stated in meters per second. PWV is a direct indicator for the arterial stiffness of the patient.
- Central Pulse Wave Velocity (cPWV): The PWV can be measured for different sections of the vascular system. If not otherwise stated, the term PWV usually refers to the cPWV, which is the PWV in the large arteries of the thorax, mainly the aorta.
- Reflection Index (RI): Is the relation between the amplitude height of the pulse wave and the height of its dicrotic wave. It is an indicator for the stiffness of the artery.
- Stiffness Index (SI): Is the relation between the amplitude height of the pulse wave and the time delay between systolic and diastolic peaks. It is an indicator for the stiffness of the artery and correlates with the cPWV.
The following reference values can be applied to these parameters:
| Parameter | Normal | Uncertain* | Pathologic |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ankle-Brachial-Index (ABI) | ≥ 1 | 1 – 0.9 | < 0.9 |
| Toe-Brachial-Index (TBI) | ≥ 0.7 | < 0.7 | |
| Pulse Wave Index (PWI™) | < 180 | 180 – 220 | > 220 |
| Toe Pressure | > 50 mmHg | 30 – 50 mmHg | < 30 mmHg |
| Rise Time | < 200 ms | 200 – 220 ms | > 200 ms |
| Rise-to-Fall Ratio | < 33 % | > 33 % | |
| Time Shift | < 40 ms | 40 – 50 ms | > 50 ms |
| Side Differences (Amplitude/Rise Time) | < 30 % | 30 – 40 % | > 40 % |
| Pulse Wave Velocity (PWV | < 10 m/s | > 10 m/s |
* If the oscillometry results in uncertain values, the measurement should be repeated after a physical stress test to obtain a trusted diagnosis.
Interpretation Criteria
When interpreting arterial or venous measurement results, the comparison between left and right side as well as the quality of the pulse wave itself plays an important role.