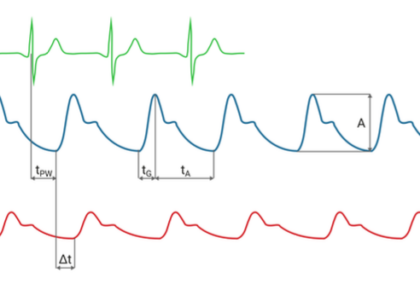
Guide on Effective PAD Screening
Download the comprehensive guide with focused contents on PAD screening: Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD) Symptoms of PAD Treatment of PAD How to assess PAD The traditional method: Ankle Brachial Index (ABI) The modern approach: Pulse Wave Index (PWI™) Vascular Screening with the TOPP-Method Measurement Principle Obtained Parameters Interpretation Example Case Study with Angiography Bonus: Exercise […]