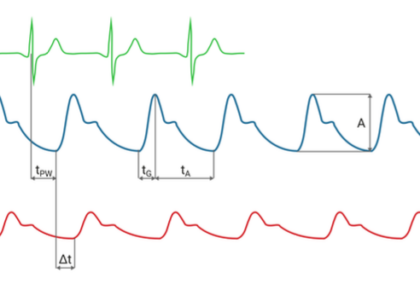
Pulse Wave Parameters
Additional key parameters and indicators can be derived from recorded pulse waves and ECG tracks: Amplitude A: The height from the beginning of the steepest rise to the highest point of the pulse curve is the amplitude. Oscillometric Index: The oscillometric index marks the pressure stage where the highest amplitude was measured and is comparable to […]